Hell Freezes-Over as Oracle Exadata, Autonomous Database (and OCI) become Available on Google Cloud Platform
So the big news in the cloud data analytics world last week was the announcement of a new partnership between Oracle and Google Cloud, similar to the one between Oracle and Microsoft back in 2022 and somewhat of a (welcome) surprise given the history between Google and Oracle over the last ten years or so.

What this means in-practice is that, today, interconnects between Oracle’s public cloud service and Google Cloud have been put in-place in a number of regional datacentres that enable low-latency, free-of-charge data interchange between services running on Oracle and Google’s cloud infrastructure.
Later on this year this partnership will expand to having Oracle’s Exadata and Autonomous Warehouse (ADW) and Autonomous Transaction Processing (ATP) database services available for licensing and deployment via Google Cloud Marketplace, enabled by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) now being available to run on servers in Google’s data centres with Oracle behind-the-scenes managing it all as afully-managed service.
Unlike before this partnership where organizations could run Oracle databases and services on Google Cloud Bare Metal Solution but in-practice didn’t because of the restrictions imposed by Oracle’s licensing and pricing policies, running Oracle Exadata and Autonomous Warehouse on Google Cloud will be fully-endorsed and supported by Oracle, will have pricing parity with OCI and, in-theory at least, will be a solution that’s jointly sold and promoted by both Oracle and Google for customers wanting a multi-cloud strategy.
As somebody working mostly in the Google Cloud and Looker ecosystem these days but who spent the the earlier part of his consulting career working with Oracle database and business intelligence technology, typically on projects using very powerful and very expensive on-premises database servers such as Oracle Exadata Database Machine (and that’s my beta program quote on the screen behind Larry, below) this was very big news.

So why exactly? Surely Oracle database, Exadata and Autonomous Data Warehouse (Oracle’s take on serverless, elastically-scalable data warehouse-platform-as-a-service) are yesterday’s news, relics of a time when databases arrived in the back of a truck and were sold and bought by the middle-aged men on golf courses that were swept-away by the dot-com revolution, the rise of consumption-based cloud computing and more recently, the modern data stack?
The reality, of course, is a bit more complex and multi-layered than that. Enterprise software and database servers like Oracle Database and Oracle Exadata are complex and expensive because the needs of enterprise customers are complex and expensive to service and sell-to.
Those customers may well have very good reasons for now to stay on Oracle platforms and services such as Oracle Exadata, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and Oracle EBS and Fusion ERP — but many of them also want to build-out their wider data analytics, data management and AI platform on a cloud-native infrastructure platform such as Google Cloud and, over time migrate their legacy Oracle workload to Google Cloud services and open-up use-cases such as:
Real-Time Analytics for Retailers: Retail companies using Oracle Fusion ERP can integrate their systems with Google Cloud’s BigQuery to analyze customer data and inventory in real-time. This enables them to optimize stock levels, predict future demand more accurately, and enhance customer satisfaction by personalizing offers and services.

Predictive Maintenance for Manufacturers: Manufacturing firms utilizing Oracle EBS can employ Google Cloud’s AI tools to predict equipment failures before they occur. By analyzing historical maintenance data and machine performance, AI models can forecast potential breakdowns, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Customer Insights for Financial Services: Financial institutions using Oracle CRM can leverage Google Cloud’s AI capabilities to gain deeper insights into customer behavior. By analyzing transaction data and customer interactions, banks can offer tailored financial advice, improve risk assessment, and enhance fraud detection.

Supply Chain Optimization: Companies can use AI to enhance their supply chain management within Oracle ERP systems. By integrating with Google Cloud’s AI and analytics, businesses can forecast supply needs, identify potential disruptions, and optimize logistics for cost and speed.
As a consulting business with roots in the Oracle world and years of experience now in the Google Cloud and Looker ecosystem, Rittman Analytics are ideally placed to help Oracle customers make the move over to Google Cloud’s leading-edge cloud infrastructure.
By combining our in-depth knowledge of Oracle’s database, business intelligence and data integration tools and services with our equally deep knowledge and experience of running similar and expanded workloads on Google Cloud services such as Google BigQuery, Looker, DataPlex and Dataform we’re uniquely well-placed to enable efficient migrations and multi-cloud connections for organizations looking to run Oracle on Google Cloud.
So what options are now available to Oracle customers and what would the steps in such a migration and adoption of Google Cloud services look like?
Let’s consider a scenario where an Oracle customer is currently running their data analytics and warehousing workload on customer-managed Exadata database servers in their datacentre along with commodity servers running WebLogic, Oracle Business Intelligence and Oracle Data Integrator.
Moving this workload to Google Cloud will enable them to expand capacity while lowering total cost-of-ownership and opens-up the capability to connect their Oracle data to Google Cloud Vertex AI’s generative AI models, modernise their data analytics by moving to Looker and their development workflow by switching from ODI to dbt or Dataform — but doing all of this needs to be a careful and considered step-by-step process that ensures the continuity of day-to-day operations.
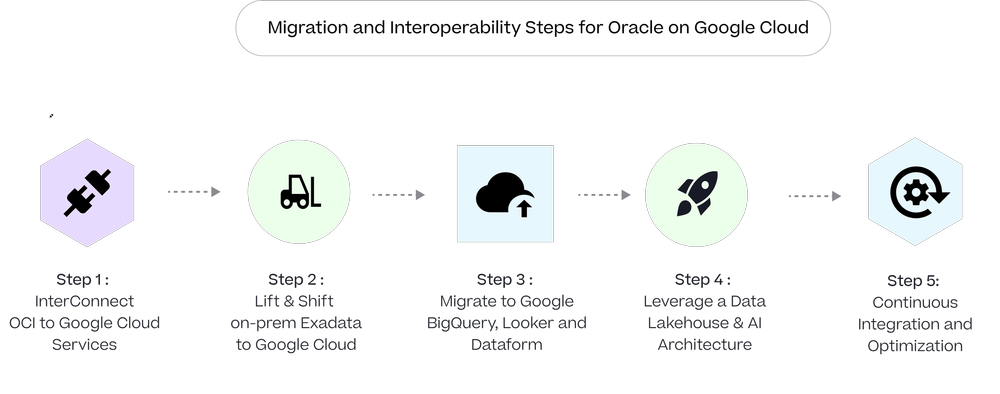
Step 1: Interconnect OCI to Google Cloud Services
The immediate opportunity now available for Oracle customers who have already moved their on-premises workload to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure running in Oracle data centres. Up until now these customers were essentially limited to using services within Oracle’s walled-garden or paying high interconnect charges (and deadling with cross-datacentre latency issues) if they wanted to take advantage of Google Cloud’s market-leading data analytics and Vertex AI services.
The new Oracle Interconnect for Google Cloud, a high-speed, low-latency connection between data and services running on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) either hosted in Oracle’s data centres or, as we’ll see in the next step, in Google’s data centres provides fast, zero-cost connectivity between these two clouds platforms.
This type of multi-cloud architecture enables you to operate a hybrid architecture where your data, analytics and transaction processing workloads stay running on Oracle database and Fusion ERP services but can now take-advantage of the advanced and more-comprehensive data analytics, data management and artificial intelligence capabilities provided by Google Cloud.
Step 2: Lift-and-Shift On-Premises Exadata to Google Cloud
For Oracle customers running Oracle Exadata on-premises and want to maintain the application compatibility, performance and capabilities of Exadata but also start to take advantage of Google Cloud’s scalability and flexibility, these workloads can be lifted-and-shifted onto Exadata Cloud service hosted on OCI in Google’s data centres and then connected to Google BigQuery, Looker and Vertex AI with zero interconnect costs or additional query latency.
Step 3 : Migrate to Google BigQuery, Looker and Dataform
While you can continue to run Exadata, Autonomous Warehouse and other Oracle services on OCI running in Google Cloud data centres, Exadata is still essentially a server-based architecture that has limits on scalability and most customers running legacy BI suites such as OBIEE are looking to move to more cutting-edge, AI-enabled modern BI services such as Looker and Looker Studio.
The next step therefore involves gradually migrating this data into Google Cloud’s BigQuery data warehouse platform service, facilitated through data integration tools and services such as Fivetran that support direct data movement from Oracle databases to BigQuery, migration of ELT and ETL transformations from ODI and OWB into dbt or Dataform and porting your business semantic layer and reports from OBIEE and BI Publisher to Looker and Looker Studio.
Step 4: Leveraging a Data Lakehouse Architecture
With your data either moved to BigQuery or left for now in Oracle databases running on Google Cloud, you can start to leverage the benefits of a data lakehouse platform as we described in our earlier blog post, “Data Lakehouses, Post-Modern Data Stacks and Enabling Gen AI: The Rittman Analytics Guide to Modernising Data Analytics in 2024”
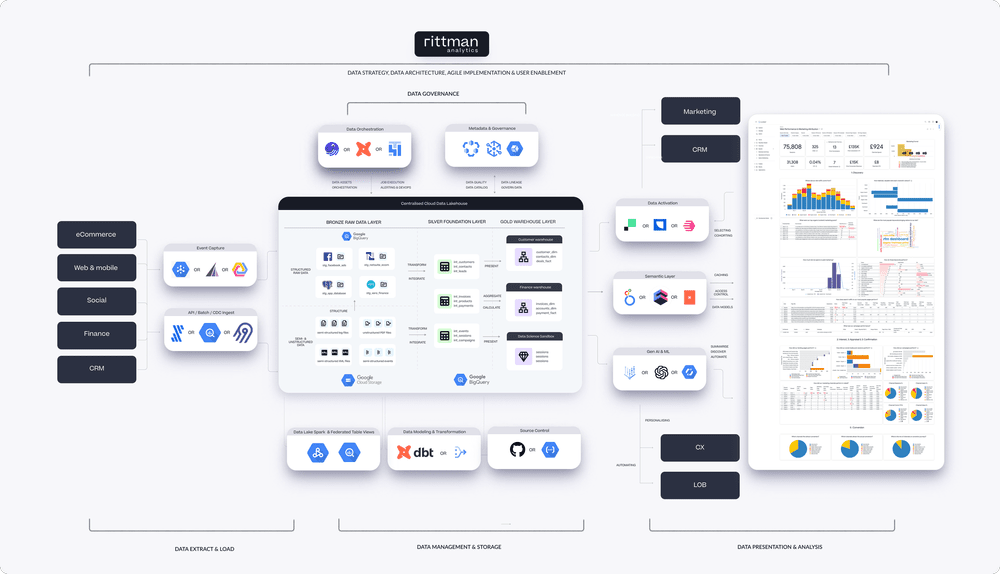
This type of data analytics and AI architecture combines the benefits of data lakes and data warehouses, offering a unified platform for managing structured and unstructured data. BigQuery’s capabilities will allow you to perform advanced analytics, machine learning, and AI on a larger, more diverse dataset.
Step 5 : Continuous Integration and Optimization
Throughout this process, the ability you now have to run Oracle Exadata as a service on Google Cloud provides a continuous operational model that can support specific workloads which may not initially migrate to BigQuery. Over time, as compatibility and performance optimization between Oracle databases and Google BigQuery are enhanced, more workloads can be transitioned into the BigQuery environment, fully adopting the data lakehouse model.
Interested? Find Out More!
Rittman Analytics is a Google Cloud Specialized Data Analytics Partner and Oracle Partner Network partner with over 25 years experience working with Oracle, Google Cloud and other leading modern data stack technologies.
With our deep expertise in both Oracle and Google Cloud technologies, we are ideally positioned to help you maximize the benefits of this partnership, ensuring a smooth transition and optimized implementation of your cloud strategies. Whether it’s executing a seamless migration or harnessing the power of advanced analytics and AI, our team is here to guide you through every step of the journey.
If you’re looking for some help and assistance moving, connecting or migrating your Oracle database, data warehousing and data analytics services over to Google Cloud or to help build-out your analytics capabilities and data team using a modern, flexible and modular data stack, contact us now to organise a 100%-free, no-obligation call — we’d love to hear from you!
Recommended Posts
One Person Many Roles: Designing a Unified Person Dimension in Google BigQuery
Why We’ve Tried to Replace Data Analytics Developers Every Decade Since 1974
How Rittman Analytics uses AI-Augmented Project Delivery to Provide Value to Users, Faster
